Head Trauma
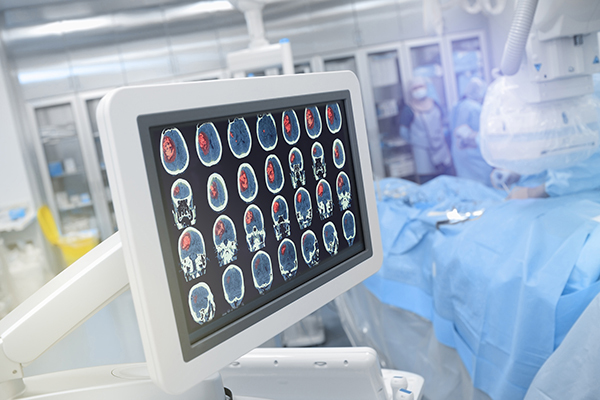
If you receive a hard blow to the head, it’s very important that you seek emergency treatment immediately, even if you don’t have any immediate symptoms. The same holds true if the blow is not hard but produces bleeding, loss of consciousness, severe headache, repeated vomiting, confusion, loss of balance, weakness in an arm or leg, unequal pupil size, slurred speech, or seizure.
This is because you may have sustained a traumatic brain injury (TBI). A TBI is a blow to the head or a penetrating head injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a TBI can be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the damage to the brain. A person with a mild TBI may remain conscious or may experience a loss of consciousness for a few seconds or minutes while someone with severe TBI may lose consciousness completely.
- Headache
- Confusion
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision or tired eyes
- Ringing in the ears
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Fatigue or lethargy
- Change in sleep patterns
- Behavioral or mood changes
- Trouble with memory, concentration, attention, or thinking
A person with a moderate or severe TBI may show these same symptoms, but may also present additional symptoms that can include:
- A headache that gets worse or doesn’t go away
- Repeated vomiting or nausea
- Convulsions or seizures
- Unable to awaken from sleep
- Dilation of one or both pupils of the eyes
- Slurred speech
- Weakness or numbness in the extremities
- Loss of coordination
- Confusion, restlessness, or agitation
Treatment
Emergency surgery is indicated if a large hematoma is found on the surface of the brain. Epidural or Subdural hematomas can cause severe brain compression and dangerous elevations of intracranial pressure which are life-threatening.
Approximately 2.5 Million Americans
Sustain a TBI Every Year
Falls
This category disproportionately affects the youngest and oldest age groups.
Motor Vehicle Crashes
Crashes are the leading cause of TBI-related death for people 5-24 years.
Struck By/Against
Happens when person is unintentionally struck by another person or object.
Assaults
Most of these injuries occur to people aged 15 – 64 years of age.